Bring Your Own Device Security Strategies – Part 5

Once the objectives, user needs, and risks, have been determined, a policy developed and the impact of deploying a BYOD solution on the enterprise has been comprehended it is time to decide on forms of deployment.
Deployment approaches
The most popular deployment approaches for BYOD are:
- Web browser access
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure / Remote Desktop
- Bootable OS
- Mobile Application Management
- Mobile Device Management
- Mobile Hybrid solutions
Web browser access
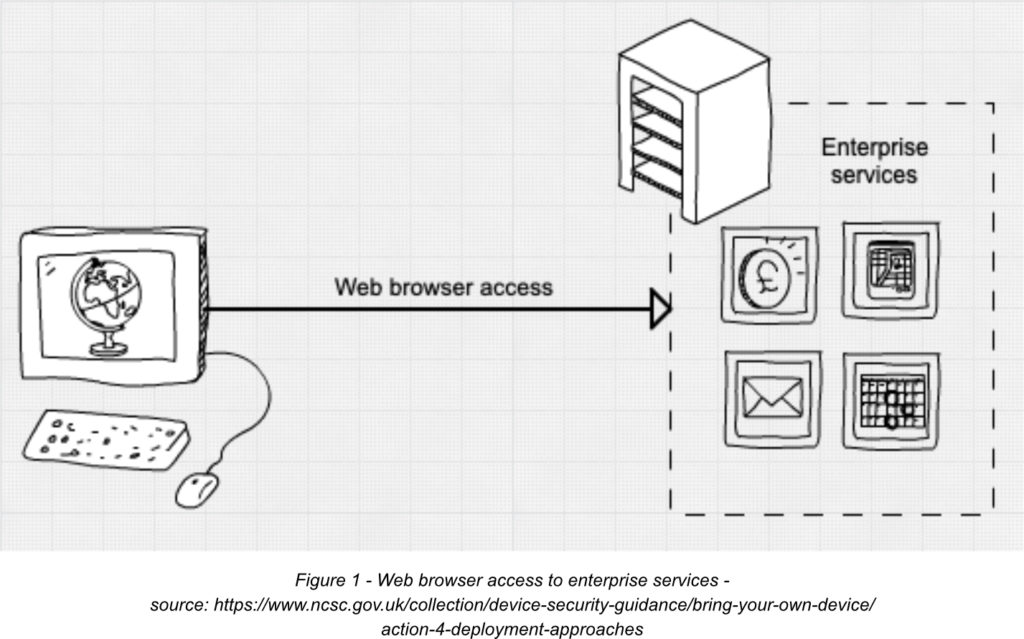
Without a doubt, this is the simplest type of BYOD solution, where users can access corporate data and services through a web browser authenticating to SaaS applications.
The unquestioned advantage of this solution is simple and versatile access and the browser’s ability to cache and recover from temporary loss of internet connectivity.
The disadvantages however include:
- Storage of some degree of corporate data on the user device makes the data potentially vulnerable
- Limited possibility to influence the security or configuration of user device
- Easy access to corporate data and credentials in case the end user’s device gets infected by malware
To improve the security of web browsers used for BYOD it is advisable to:
- Enforce strong authentication controls on corporate services such as MFA
- Ensure any Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB) used to control session-level privileges in corporate services have permissions set appropriately
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure / Remote Desktop
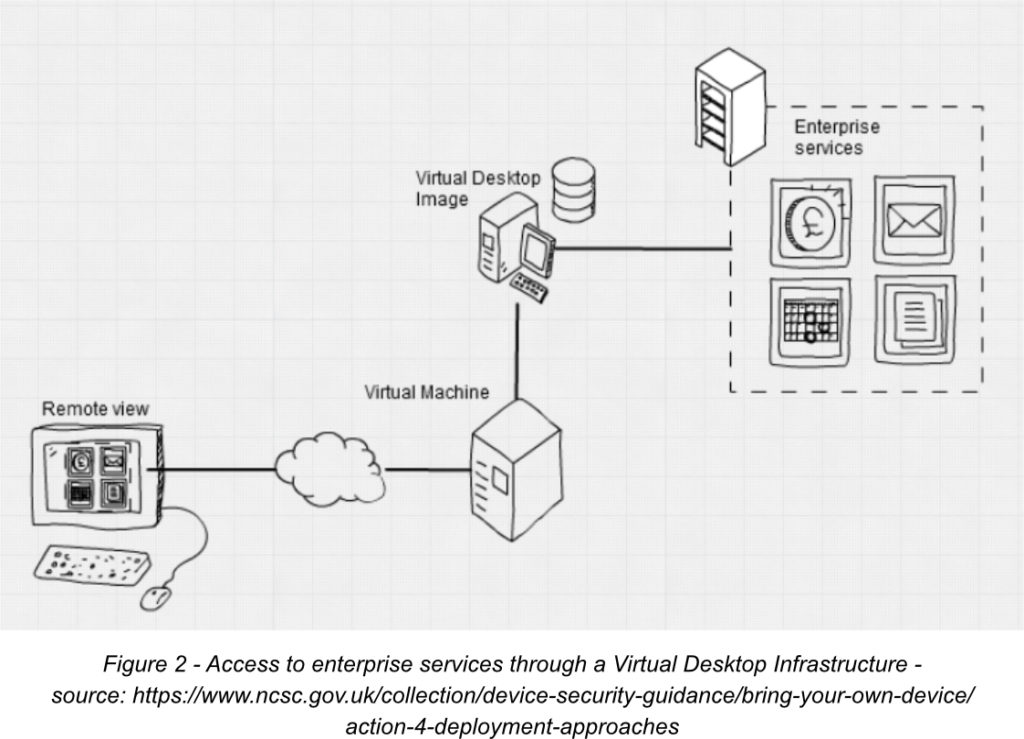
In this solution, the attack surface accessible from the internet is reduced as the user can access enterprise data and services through an interactive view of a corporate desktop defined and managed by the enterprise.
The focus here is on securing the corporate infrastructure and resources that the enterprise can control rather than using devices that it can’t.
The advantages of this approach include:
- A minimal amount of corporate data is stored on the user’s device in the well-configured virtual environment making it less likely for the data to be compromised even in the event of loss or theft of the device
- Ability to introduce controls to lower the risk of corporate data leakage to a personal application
- Ability to introduce user device and app compliance checks, and strong authentication for access
The biggest disadvantage here is the dependency on a strong and stable connection to a remote environment.
Poorly configured Remote Desktop solutions can be an initial access vector in ransomware attacks or installing other malware capable of screenscape (capture what is displayed to the user), key log (capture the input of pressed keys), or injecting keystrokes/mouse movements leading to the execution of software on the remote machine.
The technical controls available here to enforce the BYOD policy can be:
- Limiting access from legacy operating systems, browsers and authentication protocols
- Enforcing strong authentication for access to corporate resources
- Using sign-in risk assessment tools
- Preventing multiple user sessions whenever possible
- Blocking direct RDP access within the VDI
- Using controls that minimise the effect of theft of the device and/or credentials
- Gaining as much device assurance as possible
- Set idle times and act when these times are up
- Disallowing users to install unapproved software directly into the virtual environment
- Using controls to limit the sharing or removal of corporate data outside of the VDI
- Encrypting corporate data in transit and at rest
- Using logging to track all activities related to the VDI environment
In next week’s blog, we will look at other deployment approaches for BYOD.





0 Comments